Python基本数据类型(一),Python数据类型(,目录:1、运算符2、
Python基本数据类型(一),Python数据类型(,目录:1、运算符2、
目录:
1、运算符
2、type()、dir()、help()函数
3、基本数据类型常用功能之int、str操作.
正文:
一、运算符
算术运算:
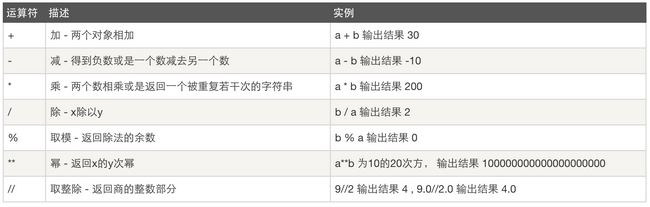
比较运算:
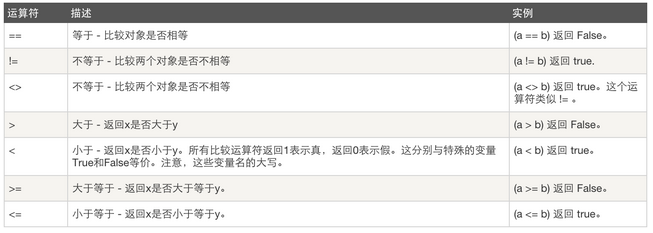
赋值运算:
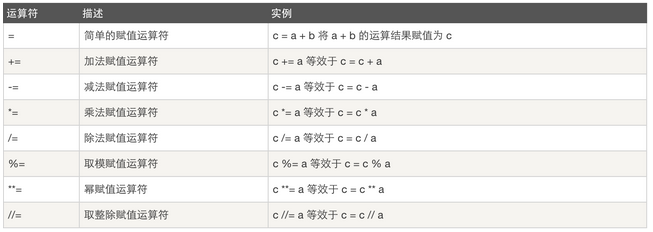
布尔操作符(逻辑运算):
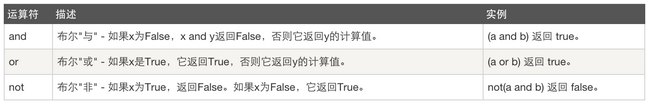
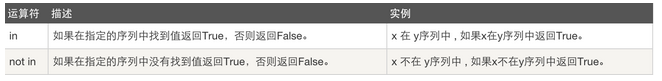
成员运算:
二、type()、dir()、help()函数
1、type()函数用来判断数据类型
>>>type(123)<class‘int‘>>>>type(123.0)<class‘float‘>>>>type("123")<class‘str‘>>>>>>>a="yangbin">>>type(a)isintFalse>>>type(a)isstrTrue>>>注: 还有一种判断数据类型的方法:isinstance()函数.
>>>a‘yangbin‘>>>isinstance(a,str)True>>>isinstance(a,int)False>>>
对于type()和isinstance()两者的区别,就是对于subclass之类的类型判断时type就不行了,必须用isinstance来判断。此处用type()即可,之后会再次提到。
2、dir()函数用来查看对像内所有属性及方法。
python内置方法有很多,无论是初学还是经通python的程序员都不能全部记住所有方法,这时候dir()函数就非常有用了。在python中任何东西都是对像,一种数据类型,一个模块等,都有自己的属性和方法,除了常用方法外,其它的不需要全部记住,交给dir()函数就好了。
>>>dir(int)[‘__abs__‘,‘__add__‘,‘__and__‘,‘__bool__‘,‘__ceil__‘,‘__class__‘,‘__delattr__‘,‘__dir__‘,‘__divmod__‘,‘__doc__‘,‘__eq__‘,‘__float__‘,‘__floor__‘,‘__floordiv__‘,‘__format__‘,‘__ge__‘,‘__getattribute__‘,‘__getnewargs__‘,‘__gt__‘,‘__hash__‘,‘__index__‘,‘__init__‘,‘__int__‘,‘__invert__‘,‘__le__‘,‘__lshift__‘,‘__lt__‘,‘__mod__‘,‘__mul__‘,‘__ne__‘,‘__neg__‘,‘__new__‘,‘__or__‘,‘__pos__‘,‘__pow__‘,‘__radd__‘,‘__rand__‘,‘__rdivmod__‘,‘__reduce__‘,‘__reduce_ex__‘,‘__repr__‘,‘__rfloordiv__‘,‘__rlshift__‘,‘__rmod__‘,‘__rmul__‘,‘__ror__‘,‘__round__‘,‘__rpow__‘,‘__rrshift__‘,‘__rshift__‘,‘__rsub__‘,‘__rtruediv__‘,‘__rxor__‘,‘__setattr__‘,‘__sizeof__‘,‘__str__‘,‘__sub__‘,‘__subclasshook__‘,‘__truediv__‘,‘__trunc__‘,‘__xor__‘,‘bit_length‘,‘conjugate‘,‘denominator‘,‘from_bytes‘,‘imag‘,‘numerator‘,‘real‘,‘to_bytes‘]>>>
>>>importsys#导入一个Python模块.>>>dir()#查看该模块的属性和方法.[‘__builtins__‘,‘__doc__‘,‘__loader__‘,‘__name__‘,‘__package__‘,‘__spec__‘,‘a‘,‘sys‘]>>>
3、help()函数用来查看对象的属性和属性介绍。
>>>help(int)Helponclassintinmodulebuiltins:classint(object)|int(x=0)->integer|int(x,base=10)->integer||Convertanumberorstringtoaninteger,orreturn0ifnoarguments|aregiven.Ifxisanumber,returnx.__int__().Forfloatingpoint|numbers,thistruncatestowardszero.||Ifxisnotanumberorifbaseisgiven,thenxmustbeastring,|bytes,orbytearrayinstancerepresentinganintegerliteralinthe|givenbase.Theliteralcanbeprecededby‘+‘or‘-‘andbesurrounded|bywhitespace.Thebasedefaultsto10.Validbasesare0and2-36.|Base0meanstointerpretthebasefromthestringasanintegerliteral.|>>>int(‘0b100‘,base=0)|4||Methodsdefinedhere:||__abs__(self,/)|abs(self)||__add__(self,value,/)|Returnself+value.||__and__(self,value,/)|Returnself&value.||__bool__(self,/)|self!=0||__ceil__(...)|CeilingofanIntegralreturnsitself.||__divmod__(self,value,/)|Returndivmod(self,value).||__eq__(self,value,/)|Returnself==value.||__float__(self,/)|float(self)...
总的来说,help()函数的查询结果更全面,包括了dir()的查询结果。
三、基本数据类型常用功能之int、str操作.
1、int类型的常用功能:
查看都有哪些功能:
>>>dir(int)...
查看各功能的用法:
>>>help(int)...
a. bit_length
功能:返回表示该数字的时占用的最少位数
>>>help(int.bit_length)Helponmethod_descriptor:bit_length(...)int.bit_length()->intNumberofbitsnecessarytorepresentselfinbinary.>>>bin(37)‘0b100101‘>>>(37).bit_length()6
例:
>>>a=21>>>bin(a)‘0b10101‘>>>a.bit_length()5>>>
b. __abs__
功能:取绝对值。
>>>help(int.__abs__)Helponwrapper_descriptor:__abs__(self,/)abs(self)
例:
>>>a=-2>>>abs(a)2>>>a.__abs__()2>>>
c. __add__
功能:相加求和
>>>help(int.__add__)Helponwrapper_descriptor:__add__(self,value,/)Returnself+value.
例:
>>>num=100>>>num.__add__(10)110>>>
d. __and__
功能:位运算
>>>help(int.__and__)Helponwrapper_descriptor:__and__(self,value,/)Returnself&value.
例:
>>>a=12>>>b=11>>>a.__and__(b)8>>>>>>a12>>>b11>>>a&b8>>>
解释:
变量a和变量b的二进制格式如下:
a=1100
b=1011
a和b相与,得到的结果为1000,换算成十进制为8.
注: 按位与运算符:参与运算的两个值,如果两个相应位都为1,则该位的结果为1,否则为0.
2、str类型的常用功能:
查看都有哪些功能:
>>>dir(str)...
查看各功能的用法:
>>>help(str)...
a. __add__
功能:把两字符串组合在一起。
>>>help(str.__add__)Helponwrapper_descriptor:__add__(self,value,/)Returnself+value.
例:
>>>a="learn">>>b="python">>>a.__add__(b)‘learnpython‘>>>b="python">>>a.__add__(b)‘learnpython‘>>>
b. __contains__
功能:判断key是否在self中,返回True或False.
>>>help(str.__contains__)Helponwrapper_descriptor:__contains__(self,key,/)Returnkeyinself.
例如:
>>>a="python">>>b="Ilikepython">>>b.__contains__(a)#b表示self,a表示key.True>>>>>>a‘python‘>>>b‘Ilikepython‘>>>ainbTrue>>>
c. __len__
功能:返回字符串的长度.
>>>help(str.__len__)Helponwrapper_descriptor:__len__(self,/)Returnlen(self).
例:
>>>num="python">>>num.__len__()6>>>len(num)6>>>
d. __lt__
功能:返回self小于value的值,成立则返回True,否则返回False.
>>>help(str.__lt__)Helponwrapper_descriptor:__lt__(self,value,/)Returnself<value.
例:
>>>a="Python">>>b="pythonn">>>a.__lt__(b)True>>>>>>a<bTrue>>>
e. isalnum
功能: 判断变量里面包含字母或数字,就返回True,否则返回False.
>>>help(str.isalnum)Helponmethod_descriptor:isalnum(...)S.isalnum()->boolReturnTrueifallcharacters(字符)inSarealphanumeric(数字字母)andthereisatleastonecharacterinS,Falseotherwise.
例:
>>>a="python">>>a.isalnum()True>>>a="python123">>>a.isalnum()True>>>
f. isalpha
功能: 判断变量里面包含字母,就返回True,否则返回False.
>>>help(str.isalpha)Helponmethod_descriptor:isalpha(...)S.isalpha()->boolReturnTrueifallcharactersinSarealphabetic(字母)andthereisatleastonecharacterinS,Falseotherwise.
例:
>>>a‘python123‘>>>a.isalpha()False#变量a中有数字,返回False.>>>b="python">>>b.isalpha()True>>>
g. isdigit
功能: 判断变量里面包含数字,就返回True,否则返回False.
>>>help(str.isdigit)Helponmethod_descriptor:isdigit(...)S.isdigit()->boolReturnTrueifallcharactersinSaredigits(数字)andthereisatleastonecharacterinS,Falseotherwise.
例:
>>>a‘python123‘>>>a.isdigit()False#变量a中包含字母,返回“False”.>>>b=123>>>b.isdigit#变量b是int类型,不被允许.Traceback(mostrecentcalllast):File"<stdin>",line1,in<module>AttributeError:‘int‘objecthasnoattribute‘isdigit‘>>>c="123"#变量c中的数字时str类型,返回True.>>>c.isdigit()True>>>
h. count
功能:用于统计字符串里某个字符出现的次数。可选参数为在字符串搜索的开始与结束位置。
>>>help(str.count)Helponmethod_descriptor:count(...)S.count(sub[,start[,end]])->intReturnthenumberofnon-overlappingoccurrencesofsubstringsubinstringS[start:end].Optionalargumentsstartandendareinterpretedasinslicenotation.
例:
>>>a="Pythonth">>>a.count("th")2>>>>>>a.count("th",1,4)1>>>i. endswith
功能: 用于判断字符串是否以指定后缀结尾,如果以指定后缀结尾返回True,否则返回False。可选参数"start"与"end"为检索字符串的开始与结束位置。从start开始,不包括end.
>>>help(str.endswith)Helponmethod_descriptor:endswith(...)S.endswith(suffix[,start[,end]])->boolReturnTrueifSendswiththespecifiedsuffix,Falseotherwise.Withoptionalstart,testSbeginningatthatposition.Withoptionalend,stopcomparingSatthatposition.suffixcanalsobeatupleofstringstotry.
例:
>>>a="IlikePython">>>a.endswith("thon")True>>>a.endswith("ke",0,6)True>>>a.endswith("ke",0,5)False>>>j. encode
功能: 用encoding指定的编码格式编码字符串。errors参数可以指定不同的错误处理方案。
>>>help(str.encode)Helponmethod_descriptor:encode(...)S.encode(encoding=‘utf-8‘,errors=‘strict‘)->bytesEncodeSusingthecodecregisteredforencoding.Defaultencodingis‘utf-8‘.errorsmaybegiventosetadifferenterrorhandlingscheme.Defaultis‘strict‘meaningthatencodingerrorsraiseaUnicodeEncodeError.Otherpossiblevaluesare‘ignore‘,‘replace‘and‘xmlcharrefreplace‘aswellasanyothernameregisteredwithcodecs.register_errorthatcanhandleUnicodeEncodeErrors.
Python2版本中,字符串默认是unicode编码;
Python3版本中, 字符串默认是utf-8编码;
encode的作用是将unicode/utf-8编码转换成encoding指定的编码格式的字符串。
例:
拿Python3版本来说,字符串默认是utf-8编码;
>>>name="中国">>>a=name.encode("gbk")#此处字符串编码由utf-8转换为gbk编码.>>>ab‘\xd6\xd0\xb9\xfa‘>>>b=a.decode("gbk")#使用decode()函数解码"gbk"为系统默认的"utf-8".>>>b‘中国‘>>>k. center
功能: 返回一个原字符串居中,并使用空格填充至长度width的新字符串。默认填充字符为空格。
>>>help(str.center)Helponmethod_descriptor:center(...)S.center(width[,fillchar])->strReturnScenteredinastringoflengthwidth.Paddingisdoneusingthespecifiedfillcharacter(defaultisaspace)
例:
>>>name="python">>>name.center(15,"a")‘aaaaapythonaaaa‘>>>
l. find
功能: 用于检测字符串中是否包含子字符串 str ,如果指定 beg(开始) 和 end(结束) 范围,则检查是否包含在指定范围内,如果包含子字符串则返回开始的索引值,否则返回-1。
>>>help(str.find)Helponmethod_descriptor:find(...)S.find(sub[,start[,end]])->intReturnthelowestindexinSwheresubstringsubisfound,suchthatsubiscontainedwithinS[start:end].Optionalargumentsstartandendareinterpretedasinslicenotation.Return-1onfailure.
例:
>>>name="python">>>name‘python‘>>>name.find("y")1>>>name.find("on")4>>>name.find("py")0>>>name.find("y",1)1>>>name.find("y",3,5)-1m. rfind
功能: 返回字符串最后一次出现的位置,如果没有匹配项则返回-1。
>>>help(str.rfind)Helponmethod_descriptor:rfind(...)S.rfind(sub[,start[,end]])->intReturnthehighestindexinSwheresubstringsubisfound,suchthatsubiscontainedwithinS[start:end].Optionalargumentsstartandendareinterpretedasinslicenotation.Return-1onfailure.
例:
>>>name="pythonandpython">>>name.rfind("py")11>>>name.rfind("py",0,10)0>>>name.rfind("py",10,0)-1>>>name.rfind("py",10,15)11>>>n. index
功能: 检测字符串中是否包含子字符串 str,如果指定 beg(开始)和end(结束)范围,则检查是否包含在指定范围内,该方法与python find()方法一样,区别在于如果str不在 string中会报一个异常。
>>>help(str.index)Helponmethod_descriptor:index(...)S.index(sub[,start[,end]])->intLikeS.find()butraiseValueErrorwhenthesubstringisnotfound.
例:
>>>name="pythonandpython">>>name.index("th")2>>>name.index("th",3)13>>>name.index("th",3,9)#要查询的字符串不在指定范围内,报错。Traceback(mostrecentcalllast):File"<stdin>",line1,in<module>ValueError:substringnotfound>>>name.index("th",3,len(name))13>>>o. rindex
功能: 返回子字符串str在字符串中最后出现的位置,如果没有匹配的字符串会报异常,可以指定可选参数[beg:end]设置查找的区间。
>>>help(str.rindex)Helponmethod_descriptor:rindex(...)S.rindex(sub[,start[,end]])->intLikeS.rfind()butraiseValueErrorwhenthesubstringisnotfound.
例:
>>>name="pythonandpython">>>name.index("th")2>>>name.rindex("th")13>>>name.rindex("th",0,13)2>>>name.rindex("th",4,10)Traceback(mostrecentcalllast):File"<stdin>",line1,in<module>ValueError:substringnotfound>>>p. isnumeric
功能: 检测字符串是否只由数字组成。如果字符串中只包含数字字符,则返回 True,否则返回 False
>>>help(str.isnumeric)Helponmethod_descriptor:isnumeric(...)S.isnumeric()->boolReturnTrueifthereareonlynumericcharactersinS,Falseotherwise.
例:
>>>name="python2017">>>name.isnumeric()False>>>name="python">>>name.isnumeric()False>>>name="2017">>>name.isnumeric()True>>>a=u‘123‘
注: 网上资料显示这种方法是只针对unicode对象,但是Python3默认为utf-8编码,并无报错。
q. islower
功能: 检测字符串是否由小写字母组成,结果返回布尔值。
>>>help(str.islower)Helponmethod_descriptor:islower(...)S.islower()->boolReturnTrueifallcasedcharactersinSarelowercaseandthereisatleastonecasedcharacterinS,Falseotherwise.
例:
>>>name="Python">>>name.islower()False>>>name="python">>>name.islower()True>>>
r. isspace
功能:检测字符串是否只由空格组成。
>>>help(str.isspace)Helponmethod_descriptor:isspace(...)S.isspace()->boolReturnTrueifallcharactersinSarewhitespaceandthereisatleastonecharacterinS,Falseotherwise.
例:
>>>name="">>>name.isspace()True>>>name="s">>>name.isspace()False>>>
s. istitle
功能:检测字符串中所有的单词拼写首字母是否为大写,且其他字母为小写。
>>>help(str.istitle)Helponmethod_descriptor:istitle(...)S.istitle()->boolReturnTrueifSisatitlecasedstringandthereisatleastonecharacterinS,i.e.upper-andtitlecasecharactersmayonlyfollowuncasedcharactersandlowercasecharactersonlycasedones.ReturnFalseotherwise.
例:
>>>name="python">>>name.istitle()False>>>name="Python">>>name.istitle()True>>>name="Python12">>>name.istitle()True>>>
t. isupper
功能:检测字符串中所有的字母是否都为大写。
>>>help(str.isupper)Helponmethod_descriptor:isupper(...)S.isupper()->boolReturnTrueifallcasedcharactersinSareuppercaseandthereisatleastonecasedcharacterinS,Falseotherwise.
例:
>>>name="Python">>>name.isupper()False>>>name="PYTHON">>>name.isupper()True>>>
u. join
功能:用于将序列中的元素以指定的字符连接生成一个新的字符串。
>>>help(str.join)Helponmethod_descriptor:join(...)S.join(iterable)->strReturnastringwhichistheconcatenationofthestringsintheiterable.TheseparatorbetweenelementsisS.
例:
>>>n1=".">>>n2="@">>>name=("P","y","t","h","o","n")>>>n1.join(name)‘P.y.t.h.o.n‘>>>n2.join(name)‘[email protected]@[email protected]@[email protected]‘>>>v. replace
功能: 把字符串中的old(旧字符串)替换成new(新字符串),如果指定第三个参数max,则替换不超过 max 次。
>>>help(str.replace)Helponmethod_descriptor:replace(...)S.replace(old,new[,count])->strReturnacopyofSwithalloccurrencesofsubstringoldreplacedbynew.Iftheoptionalargumentcountisgiven,onlythefirstcountoccurrencesarereplaced.
例:
>>>name="Thisisapetdog,Itisveryinteresting!">>>name‘Thisisapetdog,Itisveryinteresting!‘>>>name.replace("is","was")‘Thwaswasapetdog,Itwasveryinteresting!‘>>>name.replace("is","was",2)‘Thwaswasapetdog,Itisveryinteresting!‘#设定替换不超过两次,则第三次没有被替换。>>>w. split
功能: 指定分隔符对字符串进行切片,如果参数num有指定值,则仅分隔 num 个子字符串.
>>>help(str.split)Helponmethod_descriptor:split(...)S.split(sep=None,maxsplit=-1)->listofstringsReturnalistofthewordsinS,usingsepasthedelimiterstring.Ifmaxsplitisgiven,atmostmaxsplitsplitsaredone.IfsepisnotspecifiedorisNone,anywhitespacestringisaseparatorandemptystringsareremovedfromtheresult.
例:
>>>name="I‘mlearningpython">>>name.split("")["I‘m",‘learning‘,‘python‘]>>>name.split("n")["I‘mlear",‘i‘,‘gpytho‘,‘‘]>>>name.split("n",1)["I‘mlear",‘ingpython‘]>>>x. strip
功能:用于移除字符串头尾指定的字符(默认为空格)。
>>>help(str.strip)Helponmethod_descriptor:strip(...)S.strip([chars])->strReturnacopyofthestringSwithleadingandtrailingwhitespaceremoved.IfcharsisgivenandnotNone,removecharactersincharsinstead.
例:
>>>n1="Python">>>n2="###Python###">>>n1.strip()‘Python‘>>>n2.strip("#")‘Python‘>>>---END.
本文出自 “yangbin” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://13683137989.blog.51cto.com/9636221/1911393
Python基本数据类型(一)
相关内容
- 暂无相关文章
评论关闭