短时傅里叶变换(Short Time Fourier Transform)原理及 Python 实现,fouriertransform,原理 短时傅里叶变
短时傅里叶变换(Short Time Fourier Transform)原理及 Python 实现,fouriertransform,原理 短时傅里叶变
原理
短时傅里叶变换(Short Time Fourier Transform, STFT) 是一个用于语音信号处理的通用工具.它定义了一个非常有用的时间和频率分布类, 其指定了任意信号随时间和频率变化的复数幅度. 实际上,计算短时傅里叶变换的过程是把一个较长的时间信号分成相同长度的更短的段, 在每个更短的段上计算傅里叶变换, 即傅里叶频谱.
短时傅里叶变换通常的数学定义如下:
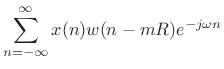
其中,

DTFT (Decrete Time Fourier Transform) 为离散时间傅里叶变换. 其数学公式, 如下所示:
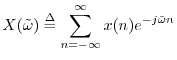
其中, x(n) 为在采样数 n 处的信号幅度. ω~ 的定义如下:
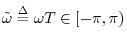
实现时, 短时傅里叶变换被计算为一系列加窗数据帧的快速傅里叶变换 (Fast Fourier Transform, FFT),其中窗口随时间 “滑动” (slide) 或“跳跃” (hop) 。
Python 实现
在程序中, frame_size 为将信号分为较短的帧的大小, 在语音处理中, 通常帧大小在 20ms 到 40ms 之间. 这里设置为 25ms, 即 frame_size = 0.025;
frame_stride 为相邻帧的滑动尺寸或跳跃尺寸, 通常帧的滑动尺寸在 10ms 到 20ms 之间, 这里设置为 10ms, 即 frame_stride = 0.01. 此时, 相邻帧的交叠大小为 15ms;
窗函数采用汉明窗函数 (Hamming Function) ;
在每一帧, 进行 512 点快速傅里叶变换, 即 NFFT = 512. 具体程序如下:
# -*- coding: utf8 -*-import numpy as npdef calc_stft(signal, sample_rate=16000, frame_size=0.025, frame_stride=0.01, winfunc=np.hamming, NFFT=512): # Calculate the number of frames from the signal frame_length = frame_size * sample_rate frame_step = frame_stride * sample_rate signal_length = len(signal) frame_length = int(round(frame_length)) frame_step = int(round(frame_step)) num_frames = 1 + int(np.ceil(float(np.abs(signal_length - frame_length)) / frame_step)) # zero padding pad_signal_length = num_frames * frame_step + frame_length z = np.zeros((pad_signal_length - signal_length)) # Pad signal to make sure that all frames have equal number of samples # without truncating any samples from the original signal pad_signal = np.append(signal, z) # Slice the signal into frames from indices indices = np.tile(np.arange(0, frame_length), (num_frames, 1)) + np.tile(np.arange(0, num_frames * frame_step, frame_step), (frame_length, 1)).T frames = pad_signal[indices.astype(np.int32, copy=False)] # Get windowed frames frames *= winfunc(frame_length) # Compute the one-dimensional n-point discrete Fourier Transform(DFT) of # a real-valued array by means of an efficient algorithm called Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) mag_frames = np.absolute(np.fft.rfft(frames, NFFT)) # Compute power spectrum pow_frames = (1.0 / NFFT) * ((mag_frames) ** 2) return pow_framesif __name__ == ‘__main__‘: import scipy.io.wavfile import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # Read wav file # "OSR_us_000_0010_8k.wav" is downloaded from http://www.voiptroubleshooter.com/open_speech/american.html sample_rate, signal = scipy.io.wavfile.read("OSR_us_000_0010_8k.wav") # Get speech data in the first 2 seconds signal = signal[0:int(2. * sample_rate)] # Calculate the short time fourier transform pow_spec = calc_stft(signal, sample_rate) plt.imshow(pow_spec) plt.tight_layout() plt.show()参考资料
1. DISCRETE TIME FOURIER TRANSFORM (DTFT).https://www.dsprelated.com/freebooks/mdft/Discrete_Time_Fourier_Transform.html
2. THE SHORT-TIME FOURIER TRANSFORM.https://www.dsprelated.com/freebooks/sasp/Short_Time_Fourier_Transform.html
3. Short-time Fourier transform.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Short-time_Fourier_transform
4.Speech Processing for Machine Learning: Filter banks, Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs) and What‘s In-Between.https://haythamfayek.com/2016/04/21/speech-processing-for-machine-learning.html
短时傅里叶变换(Short Time Fourier Transform)原理及 Python 实现
相关内容
- Python replace()方法,pythonreplace方法,描述Python r
- Python----DFS---骑士周游问题,,这篇文章将会将一个数
- python学习,,1。pycharm在
- python3写的一个检测远程服务器端口脚本,python3服务器
- pip 升级 Appium-Python-Client,,第一种方法:pip
- python 删除字典某个key(键)及对应值,pythonkey,删除字典元
- 阿里云WindowsServer部署python scrapy爬虫,,*本文适合Pytho
- python中使用指定GPU,python使用指定GPU,import oso
- python3开发进阶-Django框架中form的校验方法is_valid()的源码
- python + selenium 模拟键盘升级版PyUserInput,,前言在web自动
评论关闭