利用python数据分析panda学习笔记之基本功能,,1 重新生成索引 如
利用python数据分析panda学习笔记之基本功能,,1 重新生成索引 如
1 重新生成索引 如果某个索引值不存在就引入缺失值
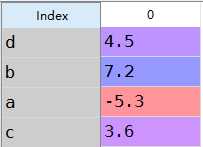
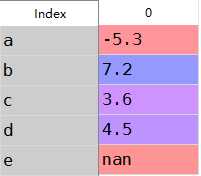
1 from pandas import Series,DataFrame2 import pandas as pd3 import numpy as np4 obj=Series([4.5,7.2,-5.3,3.6],index=[‘d‘,‘b‘,‘a‘,‘c‘])5 obj6 7 #重新生成索引8 obj2=obj.reindex([‘a‘,‘b‘,‘c‘,‘d‘,‘e‘])9 obj2
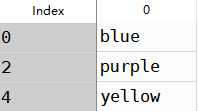
a使用method的ffill可以实现前向值填充,效果如下
1 #前向填充2 obj3=Series([‘blue‘,‘purple‘,‘yellow‘],index=[0,2,4])3 obj3.reindex(range(6),method=‘ffill‘)

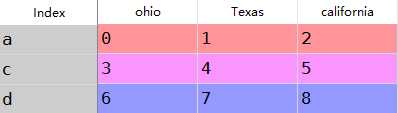
b:对于dataframe使用reindex可以同时修改行列索引,如果仅传入一个序列那么如下
1 frame=DataFrame(np.arange(9).reshape((3,3)),index=[‘a‘,‘c‘,‘d‘],2 columns=[‘ohio‘,‘Texas‘,‘california‘])3 frame
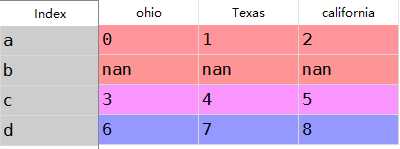
1 frame2=frame.reindex([‘a‘,‘b‘,‘c‘,‘d‘])2 frame2
c:使用colunms重新索引列
1 states=[‘Texax‘,‘Utah‘,‘california‘]2 frame.reindex(columns=states)
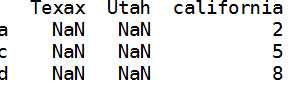
d:同时插入行列,但是插值只能按行应用
1 #同时对行 列进行重新索引 而插值只能引用到行2 frame.reindex(index=[‘a‘,‘b‘,‘c‘,‘d‘],method=‘ffill‘,3 columns=states)

reindex的参数说明如下:

2 丢弃制定轴上的项
a:drop方法返回一个指定轴上删除了指定值的新对象,删除列c
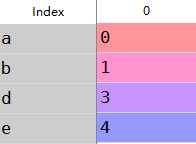
1 #丢弃指定轴的项2 obj=Series(np.arange(5.),index=[‘a‘,‘b‘,‘c‘,‘d‘,‘e‘])3 new_obj=obj.drop(‘c‘)4 new_obj
b:删除两个 b c
obj.drop([‘d‘,‘c‘])

c:对于dataframe可以删除任意轴上的索引
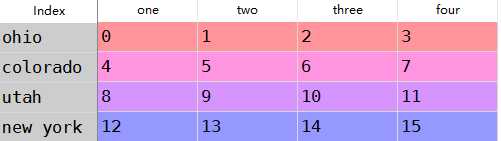
1 #对于DataFrame可以删除任意轴的索引2 data = DataFrame(np.arange(16).reshape((4,4)),3 index=[‘ohio‘,‘colorado‘,‘utah‘,‘new york‘],4 columns=[‘one‘,‘two‘,‘three‘,‘four‘])5 #删除两个6 data.drop([‘colorado‘,‘ohio‘])
3 索引,选取和过滤
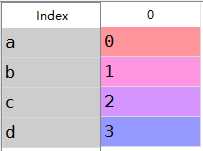
a:Series中的索引类似与Numpy,但是不只是整数,索引字符
1 obj=Series(np.arange(4.),index=[‘a‘,‘b‘,‘c‘,‘d‘])2 obj[‘b‘]#1.0
b:按照整数,范围
1 obj[1]#1.02 obj[2:4]# 2 3

c:利用标签的切片运算和普通depython切片不同,其包含末端
1 obj[‘b‘:‘c‘]#b c 1 2

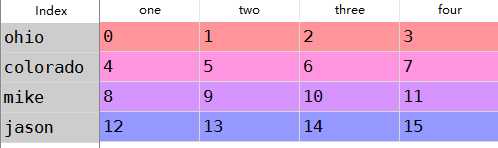
d:那么对dataframe进行索引就是获取一个或者多个列勒
1 data=DataFrame(np.arange(16).reshape(4,4),2 index=[‘ohio‘,‘colorado‘,‘mike‘,‘jason‘],3 columns=[‘one‘,‘two‘,‘three‘,‘four‘])4 data
e:选择一列
data[‘two‘]#输出第二列+行号 也就是索引
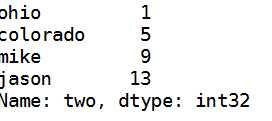
f:选择多列
1 data[[‘three‘,‘one‘]]
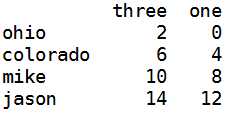
g:选取行标签前两行
data[:2]#选取的是前面两行

h:选取第三列大于5的值
data[data[‘three‘]>5]
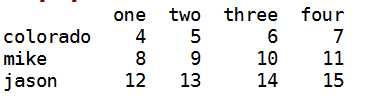
i:为了能在dataframe的行上进行标签索引引入字段ix
data.ix[‘colorado‘,[‘two‘,‘three‘]]
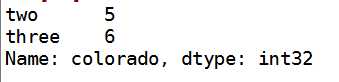
j:选取第4 1 2列 而且行为colorado jason
data.ix[[‘colorado‘,‘jason‘],[3,0,1]]
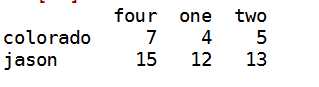
k:输出行mike
data.ix[2]
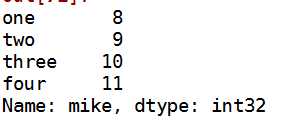
DataFrame索引总结

4 算数运算和数据对齐
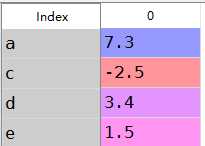
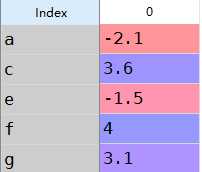
a:Series的加法
1 s1=Series([7.3,-2.5,3.4,1.5],index=[‘a‘,‘c‘,‘d‘,‘e‘])2 s2=Series([-2.1,3.6,-1.5,4,3.1],index=[‘a‘,‘c‘,‘e‘,‘f‘,‘g‘])
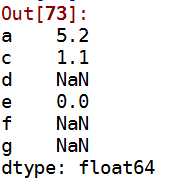
3 s1+s2
b:对于dataframe,对齐会同时发生在行 列中
df1=DataFrame(np.arange(9.).reshape((3,3)),columns=list(‘bcd‘), index=[‘utah‘,‘ohio‘,‘colorado‘])df2=DataFrame(np.arange(12.).reshape((4,3)),columns=list(‘bde‘), index=[‘utah‘,‘ohio‘,‘colorado‘,‘oragen‘])
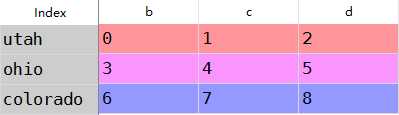
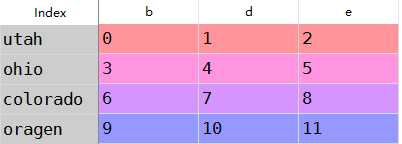
df1+df2
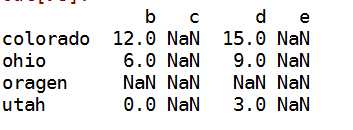
------>索引和列都为其并集
c:在算术方法中填充值。比如说两个dataframe相加,其中一个不在的时候填充为0
1 #算术中进行填充2 df1=DataFrame(np.arange(12.).reshape((3,4)),columns=list(‘abcd‘))3 df2=DataFrame(np.arange(20.).reshape((4,5)),columns=list(‘abcde‘))4 df1+df2
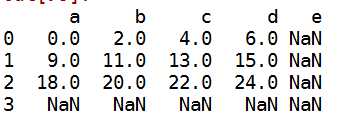
#使用df1的add方法 传入df2以及一个fill_value参数df1.add(df2,fill_value=0)
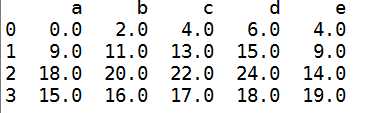
5 DataFrame和Series之间的运算----->广播,也就是如果第一个数值-1,那么这个列都会减1
a:看一看一个二维数组和一行之间的差
arr=np.arange(12.).reshape((3,4))
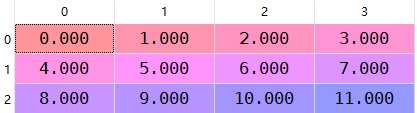
arr[0]
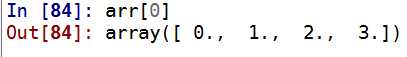
arr-arr[0]

b:frame和series的运算
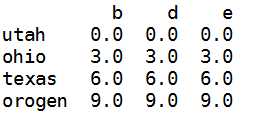
frame=DataFrame(np.arange(12.).reshape((4,3)),columns=list(‘bde‘), index=[‘utah‘,‘ohio‘,‘texas‘,‘orogen‘])series=frame.ix[0]
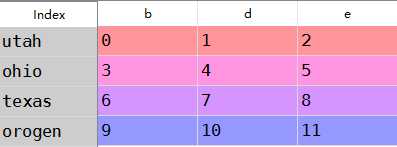
frame-series
好了,加油骚年!!!!
利用python数据分析panda学习笔记之基本功能
评论关闭