Python编写的最短路径算法,python编写最短,未经作者许可,禁止转载!
Python编写的最短路径算法,python编写最短,未经作者许可,禁止转载!
本文作者: 编橙之家 - noogel 。未经作者许可,禁止转载!欢迎加入编橙之家 专栏作者。
一心想学习算法,很少去真正静下心来去研究,前几天趁着周末去了解了最短路径的资料,用python写了一个最短路径算法。算法是基于带权无向图去寻找两个点之间的最短路径,数据存储用邻接矩阵记录。首先画出一幅无向图如下,标出各个节点之间的权值。
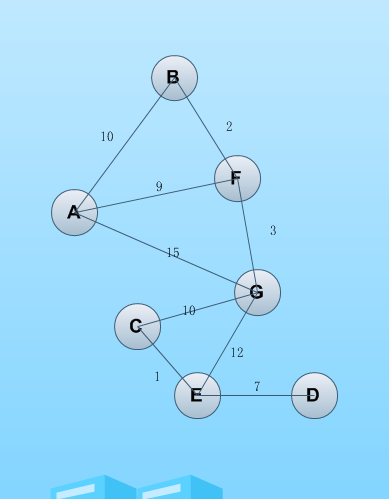
其中对应索引:
A ——> 0
B——> 1
C——> 2
D——>3
E——> 4
F——> 5
G——> 6
邻接矩阵表示无向图:
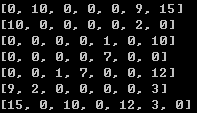
算法思想是通过Dijkstra算法结合自身想法实现的。大致思路是:从起始点开始,搜索周围的路径,记录每个点到起始点的权值存到已标记权值节点字典A,将起始点存入已遍历列表B,然后再遍历已标记权值节点字典A,搜索节点周围的路径,如果周围节点存在于表B,比较累加权值,新权值小于已有权值则更新权值和来源节点,否则什么都不做;如果不存在与表B,则添加节点和权值和来源节点到表A,直到搜索到终点则结束。
这时最短路径存在于表A中,得到终点的权值和来源路径,向上递推到起始点,即可得到最短路径,下面是代码:
Python
# -*-coding:utf-8 -*-
class DijkstraExtendPath():
def __init__(self, node_map):
self.node_map = node_map
self.node_length = len(node_map)
self.used_node_list = []
self.collected_node_dict = {}
def __call__(self, from_node, to_node):
self.from_node = from_node
self.to_node = to_node
self._init_dijkstra()
return self._format_path()
def _init_dijkstra(self):
self.used_node_list.append(self.from_node)
self.collected_node_dict[self.from_node] = [0, -1]
for index1, node1 in enumerate(self.node_map[self.from_node]):
if node1:
self.collected_node_dict[index1] = [node1, self.from_node]
self._foreach_dijkstra()
def _foreach_dijkstra(self):
if len(self.used_node_list) == self.node_length - 1:
return
for key, val in self.collected_node_dict.items(): # 遍历已有权值节点
if key not in self.used_node_list and key != to_node:
self.used_node_list.append(key)
else:
continue
for index1, node1 in enumerate(self.node_map[key]): # 对节点进行遍历
# 如果节点在权值节点中并且权值大于新权值
if node1 and index1 in self.collected_node_dict and self.collected_node_dict[index1][0] > node1 + val[0]:
self.collected_node_dict[index1][0] = node1 + val[0] # 更新权值
self.collected_node_dict[index1][1] = key
elif node1 and index1 not in self.collected_node_dict:
self.collected_node_dict[index1] = [node1 + val[0], key]
self._foreach_dijkstra()
def _format_path(self):
node_list = []
temp_node = self.to_node
node_list.append((temp_node, self.collected_node_dict[temp_node][0]))
while self.collected_node_dict[temp_node][1] != -1:
temp_node = self.collected_node_dict[temp_node][1]
node_list.append((temp_node, self.collected_node_dict[temp_node][0]))
node_list.reverse()
return node_list
def set_node_map(node_map, node, node_list):
for x, y, val in node_list:
node_map[node.index(x)][node.index(y)] = node_map[node.index(y)][node.index(x)] = val
if __name__ == "__main__":
node = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G']
node_list = [('A', 'F', 9), ('A', 'B', 10), ('A', 'G', 15), ('B', 'F', 2),
('G', 'F', 3), ('G', 'E', 12), ('G', 'C', 10), ('C', 'E', 1),
('E', 'D', 7)]
node_map = [[0 for val in xrange(len(node))] for val in xrange(len(node))]
set_node_map(node_map, node, node_list)
# A -->; D
from_node = node.index('A')
to_node = node.index('D')
dijkstrapath = DijkstraPath(node_map)
path = dijkstrapath(from_node, to_node)
print path
运行结果:

再来一例:
Python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import itertools
import re
import math
def combination(lst): # 全排序
lists = []
liter = itertools.permutations(lst)
for lts in list(liter):
lt = ''.join(lts)
lists.append(lt)
return lists
def coord(lst): # 坐标输入
coordinates = dict()
print u'请输入坐标:(格式为A:7 17)'
p = re.compile(r"d+")
for char in lst:
str = raw_input(char + ':')
dot = p.findall(str)
coordinates[char] = [dot[0], dot[1]]
print coordinates
return coordinates
def repeat(lst): # 删除重复组合
for ilist in lst:
for k in xrange(len(ilist)):
st = (ilist[k:], ilist[:k])
strs = ''.join(st)
for jlist in lst:
if(cmp(strs, jlist) == 0):
lst.remove(jlist)
for k in xrange(len(ilist)):
st = (ilist[k:], ilist[:k])
strs = ''.join(st)
for jlist in lst:
if(cmp(strs[::-1], jlist) == 0):
lst.remove(jlist)
lst.append(ilist)
print lst
return lst
def count(lst, coordinates): # 计算各路径
way = dict()
for str in lst:
str = str + str[:1]
length = 0
for i in range(len(str) - 1):
x = abs(float(coordinates[str[i]][0]) -
float(coordinates[str[i + 1]][0]))
y = abs(float(coordinates[str[i]][1]) -
float(coordinates[str[i + 1]][1]))
length += math.sqrt(x**2 + y**2)
way[str[:len(str) - 1]] = length
return way
if __name__ == "__main__":
print u'请输入图节点:'
rlist = list(raw_input())
coordinates = coord(rlist)
list_directive = combination(rlist)
# print "有方向完全图所有路径为:",list_directive
# for it in list_directive:
# print it
print u'有方向完全图所有路径总数:', len(list_directive), "n"
# 无方向完全图
list_directive = repeat(list_directive)
list_directive = repeat(list_directive)
# print "无方向完全图所有路径为:",list_directive
print u'无方向完全图所有路径为:'
for it in list_directive:
print it
print u'无方向完全图所有路径总数:', len(list_directive)
ways = count(list_directive, coordinates)
print u'路径排序如下:'
for dstr in sorted(ways.iteritems(), key=lambda d: d[1], reverse=False):
print dstr
raw_input()
以上就是本文给大家分享的全部内容了,希望大家能够喜欢,能够学习python有所帮助。
相关内容
- python实现堆排序算法代码,python堆排序算法,python 实现
- Python插入排序和堆排序,python排序堆排序,插入排序,它
- Python 模拟竖式大数乘法,python竖式大数乘法,python内置
- python解决八皇后算法,python皇后算法,python解决经典算法
- python实现逆波兰计算表达式,python波兰表达式,逆波兰表
- python实现希尔排序算法,python希尔算法,希尔排序(Shel
- python求两序列的和最小差值序列,python最小差值序列
- python实现Bogo排序算法,pythonbogo排序,Bogo算法定义下面是
- Python计算24点代码,python计算24点,下面的代码通过算2
- Python实现java或者.net的getHashCode()函数,pythongethashcode,
评论关闭