练习题|python常用模块,练习题python模块,re模块练习1.验证
练习题|python常用模块,练习题python模块,re模块练习1.验证
re模块练习
1.验证手机号是否合法
import rephone_pat = re.compile(‘^(13\d|14[5|7]\d|15\d|166|17[3|6|7]|18\d)\d{8}$‘)while True: phone = input(‘请输入您的手机号:‘) res = re.search(phone_pat, phone) if res: print(‘正常手机号‘) else: print(‘这不是一个手机号‘)‘‘‘* 手机号码* 移动:134,135,136,137,138,139,150,151,157,158,159,182,187,188* 联通:130,131,132,152,155,156,185,186* 电信:133,134,153,180,189147... 176...‘‘‘import re# phone_num = ‘13789481229‘phone_num = input(‘phone>>>:‘)# pattern = re.compile(‘^0\d{2,3}\d{7,8}$|^1[358]\d{9}$|^147\d{8}‘)pattern = re.compile(‘^1[34578]\d{9}‘)phone_match = pattern.fullmatch(phone_num)if phone_match: print(phone_match.group())else: print(‘\033[1;31mphone is error\033[0m‘)2.验证邮箱是否合法
import re# email = ‘[email protected]‘email = input(‘email>>>:‘)# pattern = re.compile(‘\[email protected]\w+\.(com|cn)‘)pattern = re.compile(‘[-_\w][email protected][-_\w]+\.(com|cn|edu)‘)email_match = pattern.fullmatch(email)if email_match: print(email_match.group())else: print(‘\033[1;31memail is error\033[0m‘) #re.match("^.+\\@(\\[?)[a-zA-Z0-9\\-\\.]+\\.([a-zA-Z]{2,3}|[0-9]{1,3})(\\]?)$", email) 3.开发一个简单的python计算器,实现加减乘除及拓号优先级解析
用户输入 1 - 2 * ( (60-30 +(-40/5) * (9-2*5/3 + 7 /3*99/4*2998 +10 * 568/14 )) - (-4*3)/ (16-3*2) )等类似公式后,必须自己解析里面的(),+,-,*,/符号和公式(不能调用eval等类似功能偷懒实现),运算后得出结果,结果必须与真实的计算器所得出的结果一致
hint:re.search(r‘\([^()]+\)‘,s).group()#可拿到最里层的括号中的值 ‘(-40/5)‘
参考http://www.bubuko.com/infodetail-1729967.html
本章总结练习
1、logging模块有几个日志级别?
logging模块共5个级别,它们分别是: DEBUG INFO WARNING ERROR CRITICAL
2、请配置logging模块,使其在屏幕和文件里同时打印以下格式的日志
2017-10-18 15:56:26,613 - access - ERROR - account [1234] too many login attempts
import logging#1.生成logger对象logger =logging.getLogger("access")logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)#2.生成handler对象ch = logging.StreamHandler()ch.setLevel(logging.ERROR) ##设置输出屏幕级别fh = logging.FileHandler("access.log") #生成文件fh.setLevel(logging.ERROR) ##设置输出文件级别#2.1把handler对象绑定到loggerlogger.addHandler(ch)logger.addHandler(fh)#3.生成formatter对象#3.1把formatter对象绑定handler对象file_formatter = logging.Formatter(‘%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s‘)console_formatter = logging.Formatter(‘%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s- %(lineno)d- %(message)s‘)ch.setFormatter(console_formatter)fh.setFormatter(file_formatter)logger.error("account [1234] too many login attempts")3、json、pickle、shelve三个区别是什么
首先,这三个模块都是序列化工具。 1. json是所有语言的序列化工具,优点跨语言、体积小.只能序列化一些基本的数据类型。int\str\list\tuple\dict pickle是python语言特有序列化工具,所有数据都能序列化。只能在python中使用,存储数据占空间大. shelve模块是一个简单的k,v将内存数据通过文件持久化的模块,可以持久化任何pickle可支持的python数据格式。 2. 使用方式,json和pickle用法一样,shelve是f = shelve.open(‘shelve_test‘)
4、json的作用是什么?
序列化是指把内存里的数据类型转变成字符串,以使其能存储到硬盘或通过网络传输到远程,因为硬盘或网络传输时只能接受bytes
5、subprocess执行命令方法有几种?
有三种方法,他们分别是 run()方法 call()方法 Popen()方法
6、为什么要设计好目录结构?
1.可读性高: 不熟悉这个项目的代码的人,一眼就能看懂目录结构,知道程序启动脚本是哪个,测试目录在哪儿,配置文件在哪儿等等。
从而非常快速的了解这个项目。2.可维护性高: 定义好组织规则后,维护者就能很明确地知道,新增的哪个文件和代码应该放在什么目录之下。
这个好处是,随着时间的推移,代码/配置的规模增加,项目结构不会混乱,仍然能够组织良好。
7、打印出命令行的第一个参数。例如
python argument.py luffy打印出 luffy
import sysprint(sys.argv[1])8、代码如下
‘‘‘Linux当前目录/usr/local/nginx/html/文件名:index.html‘‘‘import osBASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(index.html)))print(BASE_DIR)打印的内容是什么? 打印的内容是:
/usr/local/nginxos.path.dirname和os.path.abspath含义是什么? os.path.dirname是指定文件的目录;os.path.abspath指的是文件的绝对路径。9、通过configparser模块完成以下功能
文件名为my.cnf
[DEFAULT][client]port = 3306socket = /data/mysql_3306/mysql.sock[mysqld]#explicit_defaults_for_timestamp = true 要把它注释掉port = 3306socket = /data/mysql_3306/mysql.sockback_log = 80basedir = /usr/local/mysqltmpdir = /tmpdatadir = /data/mysql_3306default-time-zone = ‘+8:00‘
修改时区 default-time-zone = ‘+8:00‘ 为 校准的全球时间 +00:00import configparserconfig = configparser.ConfigParser()config.read(‘my.cnf‘)print(config[‘mysqld‘][‘default-time-zone‘] ) #08:00config.set(‘mysqld‘,‘default-time-zone‘,‘+00:00‘)config.write(open(‘my.cnf‘, "w"))print(config[‘mysqld‘][‘default-time-zone‘] ) #+00:00
删除 explicit_defaults_for_timestampimport configparserconfig = configparser.ConfigParser()config.read(‘my.cnf‘)config.remove_option(‘mysqld‘,‘explicit_defaults_for_timestamp‘)config.write(open(‘my.cnf‘, "w"))
为DEFAULT增加一条 character-set-server = utf8import configparserconfig = configparser.ConfigParser()config.read(‘my.cnf‘)config.set(‘DEFAULT‘,‘character-set-server‘,‘utf8‘)config.write(open(‘my.cnf‘, "w"))
10、写一个6位随机验证码程序(使用random模块),要求验证码中至少包含一个数字、一个小写字母、一个大写字母.
import randomimport stringa = ‘‘.join(random.sample(string.ascii_lowercase + string.ascii_uppercase + string.digits,6))print(a)
11、利用正则表达式提取到 luffycity.com ,内容如下
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>luffycity.com</title></head><body></body></html>
import ref = open(‘index.html‘,‘r‘,encoding=‘utf-8‘)data = f.read()#print(data)print(re.findall(‘luffycity.com‘, data)) #[‘luffycity.com‘]
12、写一个用户登录验证程序,文件如下
1234.json
{"expire_date": "2021-01-01", "id": 1234, "status": 0, "pay_day": 22, "password": "abc"}用户名为json文件名,密码为 password。判断是否过期,与expire_date进行对比。登陆成功后,打印“登陆成功”,三次登陆失败,status值改为1,并且锁定账号。import jsonimport timeusername = input(‘请输入用户名(文件名):‘)f = open(‘1234.json‘,‘r‘,encoding=‘utf-8‘)data = f.read()data1 = json.loads(data)#print(data1[‘password‘])count = 0while count < 3: if (int(time.strftime(‘%Y‘)))-(int(data1["expire_date"][0:4])) > 0: print(‘您的账户已过期‘) exit() if data1[‘status‘] == 1: print(‘您的账户已被锁定,无法登录‘) exit() password = input(‘请输入密码:‘) if password == data1[‘password‘]: print(‘登录成功‘) elif count == 2: data1[‘status‘] = 1 f1 = open(‘1234.json‘,‘w‘,encoding=‘utf-8‘) json.dump(data1,f1) #修改json数据 print(‘您的账户已被锁定‘) exit() else: print(‘您的密码有误,请重新输入‘) count += 1
13、把第12题三次验证的密码进行hashlib加密处理。即:json文件保存为md5的值,然后用md5的值进行验证。
"password": "900150983cd24fb0d6963f7d28e17f72"
#加入下面这个就可以password = input(‘请输入密码:‘) m = hashlib.md5() m.update(password.encode()) if m.hexdigest() == data1[‘password‘]: print(‘登录成功‘)
14、最近luffy买了个tesla,通过转账的形式,并且支付了5%的手续费,tesla价格为75万。文件为json,请用程序实现该转账行为。
需求如下:
##目录结构为├── account│ ├── luffy.json│ └── tesla.json└── bin └── start.py
当执行start.py时,出现交互窗口
------- Luffy Bank --------- 1. 账户信息 2. 转账
选择1 账户信息 显示luffy的当前账户余额。选择2 转账 直接扣掉75万和利息费用并且tesla账户增加75万15、对上题增加一个需求:提现。
目录结构如下
├── account│ └── luffy.json├── bin│ └── start.py└── core └── withdraw.py
当执行start.py时,出现交互窗口
------- Luffy Bank ---------1. 账户信息2. 提现
选择1 账户信息 显示luffy的当前账户余额和信用额度。选择2 提现 提现金额应小于等于信用额度,利息为5%,提现金额为用户自定义。16、尝试把上一章的验证用户登陆的装饰器添加到提现和转账的功能上
17、对第15题的用户转账、登录、提现操作均通过logging模块记录日志,日志文件位置如下
. ├── account │ └── luffy.json ├── bin │ └── start.py └── core | └── withdraw.py └── logs └── bank.log
14--17:
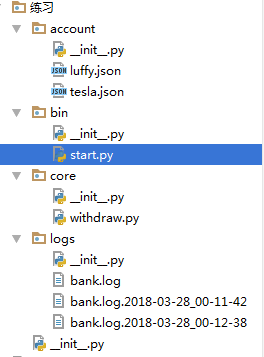
bin start.py
#Author:Kris# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-import os,sysimport jsonimport loggingfrom logging import handlerscore_path = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))sys.path.append(core_path)from core import withdraw_username = ‘alice‘_password = ‘123‘msg = ‘‘‘1. 账户信息2. 转账3. 提现‘‘‘json_path = os.path.join(core_path, ‘account‘)flag_login = Falselogger = logging.getLogger(‘record‘)def log_record(): global logger logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG) # fh = logging.FileHandler(os.path.join(core_path, ‘logs/bank.log‘),encoding=‘utf-8‘) fh = logging.handlers.TimedRotatingFileHandler(filename=os.path.join(core_path, ‘logs/bank.log‘),when=‘S‘,interval=3,backupCount=3,encoding=‘utf-8‘) logger.addHandler(fh) f_formatter = logging.Formatter(fmt=‘%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s‘,datefmt=‘%m/%d/%Y %I:%M:%S %p‘) fh.setFormatter(f_formatter)def login(func): def inner(): global flag_login if not flag_login: username = input(‘username:‘).strip() password = input(‘password:‘).strip() if username == _username and password == _password: print(‘登录成功!‘) flag_login = True logger.info(‘登录成功‘) else: print(‘用户名或密码有误!‘) else: print(‘用户已登录,通过认证‘) if flag_login is True: func() return innerdef print_info(): # 账户信息 luffy_data = json.load(open(os.path.join(json_path, ‘luffy.json‘), ‘r‘, encoding=‘utf-8‘)) print(‘account_balance:‘, luffy_data[‘account_balance‘]) print(‘credit_account:‘, luffy_data[‘credit_account‘])@logindef transfer_account(): # 转账 luffy_data = json.load(open(os.path.join(json_path, ‘luffy.json‘), ‘r‘, encoding=‘utf-8‘)) tesla_data = {‘account_balance‘: 750000} luffy_data[‘account_balance‘] = luffy_data[‘account_balance‘] - tesla_data[‘account_balance‘] * (1 + 0.05) json.dump(luffy_data, open(os.path.join(json_path, ‘luffy.json‘), ‘w‘, encoding=‘utf-8‘)) json.dump(tesla_data, open(os.path.join(json_path, ‘tesla.json‘), ‘w‘, encoding=‘utf-8‘)) print(‘转账成功!‘) logger.debug(‘转账成功‘)@logindef withdraws_func(): # 提现 moneys = input(‘moneys>>>:‘).strip() if moneys.isdigit(): moneys = int(moneys) withdraw.withdraws(moneys, json_path, logger)def main(): while True: print("Luffy Bank".center(30, ‘-‘)) print(msg) num = input(‘num(q表示退出)>>>:‘).strip() if not num: continue if num.isdigit(): num = int(num) if num == 1: # 账号信息 print_info() elif num == 2: # 转账 transfer_account() elif num == 3: # 提现 withdraws_func() elif num == ‘q‘: exit()if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: log_record() main()core withdraw.py
#Author:Kris# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-import os, jsondef withdraws(moneys, json_path, logger): luffy_data = json.load(open(os.path.join(json_path, ‘luffy.json‘), ‘r‘, encoding=‘utf-8‘)) if moneys <= luffy_data[‘credit_account‘]: luffy_data[‘credit_account‘] = luffy_data[‘credit_account‘] - moneys*(1+0.05) json.dump(luffy_data, open(os.path.join(json_path, ‘luffy.json‘), ‘w‘, encoding=‘utf-8‘)) print(‘提现成功!‘) logger.warning(‘提现成功‘) else: print(‘\033[0;31m提现金额大于信用额度了!\033[0m‘) logger.error(‘提现金额大于信用额度‘)
练习题|python常用模块
相关内容
- Python3 魔法方法:定制序列,python3定制,1、基于序列的
- Python的一个命名空间冲突,关于from-import机制,pythonf
- Sublime Text3 配置Python3编译环境,sublimepython3,Sublime Te
- python字符串替换之re.sub(),pythonre.sub,re.sub(pat
- 深度学习 GPU环境 Ubuntu 16.04 + Nvidia GTX 1080 + Python 3.6 +
- 【每日道代码题001】- PYTHON基础复习,001python,问题001
- Python在Windows下操作CH341DLL,pythonch341dll, 1 #! /usr
- 泰坦尼克号生存预测(python),泰坦尼克号python,1 数据
- Python-功能函数的使用(三),python-函数,使用可选的可
- python爬微博,python爬,# -*- codi
评论关闭