Python操作MySQL,,一、MySQL基本操
Python操作MySQL,,一、MySQL基本操
一、MySQL基本操作
1、设置root密码/修改root密码
方法一:用mysqladmin
mysqladmin -u root password "newpass"
mysqladmin -u root password oldpass "newpass"
方法二: 用set password命令(也可以用于修改密码)
mysql -u root
mysql> SET PASSWORD FOR ‘root‘@‘localhost‘ = PASSWORD(‘newpass‘);
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
方法三:用update直接编辑user表(也可以用于修改密码)
mysql -u root
mysql> UPDATE mysql.user SET Password = PASSWORD(‘newpass‘) WHERE user = ‘root‘;
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
2、破解root密码
mysqld_safe --skip-grant-tables&
mysql> UPDATE mysql.user SET password=PASSWORD("newpass") WHERE user=‘root‘;
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
3、增删改查
mysql> show databases; # 查看所有数据库mysql> create database s12day9 charset ‘utf8‘; # 创建名为s12day9的数据库,并设置字符编码为utf8
mysql> use s12day9; # 切换到s12day9数据库
mysql> create table students # 创建students表,主键为id,不能为空 -> ( -> id int not null auto_increment primary key, -> name char(32) not null, -> sex char(20) not null, -> age tinyint unsigned not null, -> tel char(13) null default "-" -> );mysql> desc students; # 查看students表结构mysql> show create table students; # 查看表详细结构语句mysql> insert into students(name,sex,age,tel) values(‘alex‘,‘boy‘,18,‘151515151‘); # 插入一条数据mysql> insert into students(name,sex,age,tel) values(‘flash‘,‘man‘,26,‘156515151‘);mysql> insert into students(name,sex,age,tel) values(‘tony‘,‘man‘,40,‘196515151‘);mysql> select * from students where age> 20; # 查询students表中年龄大于20的数据记录mysql> select * from students where age > 26 and sex = ‘man‘; mysql> select * from students where age like ‘2%‘; mysql> select name,sex from students where age like ‘2%‘;mysql> update students set age = 26 where name=‘alex‘; # 更新students表中alex年龄为26 mysql> select * from students where age like ‘2%‘;mysql> update students set age = 26; # 设置所有人的年龄都是26mysql> delete from students where name=‘tony‘; # 删除名称为tony的数据记录mysql> alter table students add column nal char(64); # 添加一条nal字段
二、Python操作MySQL
Python2中操作MySQL一般使用MySQLdb模块,MySQLdb貌似不支持Python3,所以下面的所有代码均在Python2中实现。
在CentOS系统中可以通过yum安装mysql-python获取MySQLdb模块,也可以通过pip安装umysqldb获得MySQLdb。
a) yum install mysql-python 直接导入 import MySQLdb 即可
b) pip install umysqldb
>>> import umysqldb
>>> umysqldb.install_as_MySQLdb()
>>> import MySQLdb
1、插入数据
#!/usr/bin/env python2# encoding:utf-8import MySQLdbconn = MySQLdb.connect(host=‘127.0.0.1‘,user=‘root‘,passwd=‘123,.abc‘,db=‘s12day9‘)cur = conn.cursor()reCount = cur.execute(‘insert into students(id,name,sex,age,tel,nal) values(%s,%s,%s,%s,%s,%s)‘,(4,‘eric‘,‘oldboy‘,‘40‘,‘159595959‘,‘1234‘))conn.commit()cur.close()conn.close()print reCount
批量插入数据
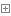
1 #!/usr/bin/env python2 2 # encoding:utf-8 3 4 import umysqldb 5 umysqldb.install_as_MySQLdb() 6 import MySQLdb 7 8 conn = MySQLdb.connect(host=‘127.0.0.1‘,user=‘root‘,passwd=‘123,.abc‘,db=‘s12day9‘) 9 10 cur = conn.cursor()11 12 li = [13 (15,‘Rambo‘,‘superman‘,‘18‘,‘18995959595‘,‘9527‘),14 (16,‘Rambo‘,‘superman‘,‘18‘,‘18995959595‘,‘9527‘),15 (17,‘Rambo‘,‘superman‘,‘18‘,‘18995959595‘,‘9527‘),16 ]17 reCount = cur.executemany(‘insert into students(id,name,sex,age,tel,nal) values(%s,%s,%s,%s,%s,%s)‘,li)18 19 conn.commit()20 21 cur.close()22 conn.close()23 24 print reCountView Code
2、查询数据
fetchone
#!/usr/bin/env python# encoding:utf-8import MySQLdb conn = MySQLdb.connect(host=‘127.0.0.1‘,user=‘root‘,passwd=‘123,.abc‘,db=‘s12day9‘)cur = conn.cursor() reCount = cur.execute(‘select * from students‘) print cur.fetchone() # 打印第1条数据 print cur.fetchone() # 打印第2条数据 cur.scroll(-1,mode=‘relative‘) # 将游标设置为相对位置,相对向上移1print cur.fetchone() # 打印的是第2条数据print cur.fetchone() # 打印第3条数据cur.scroll(0,mode=‘absolute‘) # 将游标设置为绝对位置,刻度为0print cur.fetchone() # 打印第1条数据print cur.fetchone() # 打印第2条数据 cur.close() conn.close()
fetchall
import MySQLdbconn = MySQLdb.connect(host=‘127.0.0.1‘,user=‘root‘,passwd=‘123,.abc‘,db=‘s12day9‘)cur = conn.cursor() reCount = cur.execute(‘select name,age from students‘)nRet = cur.fetchall()cur.close()conn.close()print nRetfor i in nRet: print i[0],i[1]
3、修改数据
import MySQLdbconn = MySQLdb.connect(host=‘127.0.0.1‘,user=‘root‘,passwd=‘123,.abc‘,db=‘s12day9‘)cur = conn.cursor()#reCount = cur.execute(‘update students set name = %s‘,(‘alin‘,)) reCount = cur.execute(‘update students set name = %s where id > 10‘,(‘Rambo‘,))conn.commit()cur.close()conn.close()print reCount
4、删除数据
import MySQLdbconn = MySQLdb.connect(host=‘127.0.0.1‘,user=‘root‘,passwd=‘123,.abc‘,db=‘s12day9‘)cur = conn.cursor()reCount = cur.execute(‘delete from students where name = %s‘,(‘alin‘,))conn.commit()cur.close()conn.close()print reCount
Python操作MySQL
相关内容
- 暂无相关文章
评论关闭