python之懒惰属性(延迟初始化),, Python 对
python之懒惰属性(延迟初始化),, Python 对
Python 对象的延迟初始化是指,当它第一次被创建时才进行初始化,或者保存第一次创建的结果,然后每次调用的时候直接返回该结果。延迟初始化主要用于提高性能,避免浪费计算,并减少程序的内存需求。
1. 温故下property
property可以将属性的访问转变成方法的调用
class Circle(object): def __init__(self, radius): self.radius = radius @property def area(self): return 3.14 * self.radius ** 2 c = Circle(4) print c.radius print c.area
可以看到,area虽然是定义成一个方法的形式,但是加上@property后,可以直接执行c.area,当成属性访问。
现在问题来了,每次调用c.area,都会计算一次,太浪费cpu了,怎样才能只计算一次呢?这就是lazy property
2.lazy property实现
实现延迟初始化有两种方式,一种是使用python描述符,另一种是使用@property修饰符
方法1:
class lazy(object): def __init__(self, func): self.func = func def __get__(self, instance, cls): val = self.func(instance) setattr(instance, self.func.__name__, val) return val class Circle(object): def __init__(self, radius): self.radius = radius @ lazy def area(self): print ‘evalute‘ return 3.14 * self.radius ** 2 c = Circle(4) print c.radius print c.area print c.area print c.area
结果‘evalute‘只输出了一次。在lazy类中,我们定义了__get__()方法,所以它是一个描述符。当我们第一次执行c.area时,python解释器会先从c.__dict__中进行查找,没有找到,就从Circle.__dict__中进行查找,这时因为area被定义为描述符,所以调用__get__方法。
在__get__()方法中,调用实例的area()方法计算出结果,并动态给实例添加一个同名属性area,然后将计算出的值赋予给它,相当于设置c.__dict__[‘area‘]=val。
当我们再次调用c.area时,直接从c.__dict__中进行查找,这时就会直接返回之前计算好的值了。
方法2:
def lazy_property(func): attr_name = "_lazy_" + func.__name__ @property def _lazy_property(self): if not hasattr(self, attr_name): setattr(self, attr_name, func(self)) return getattr(self, attr_name) return _lazy_property class Circle(object): def __init__(self, radius): self.radius = radius @lazy_property def area(self): print ‘evalute‘ return 3.14 * self.radius ** 2
这里与方法1异曲同工,在area()前添加@lazy_property相当于运行以下代码:
lazy_property(area)
lazy_property()方法返回_lazy_property,_lazy_property又会调用_lazy_property()方法,剩下的操作与方法1类似。
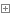
#性能差方法class Circle(object): def __init__(self, radius): self.radius = radius @property def area(self): print("come in") return 3.14 * self.radius ** 2 c = Circle(4) print(c.radius) print(c.area) print(c.area) #方法1class LazyProperty: def __init__(self, method): self.method = method def __get__(self, instance, cls): if not instance: return None value = self.method(instance) setattr(instance,self.method.__name__,value) return value class Circle(object): def __init__(self, radius): self.radius = radius @LazyProperty def area(self): print("come in") return 3.14 * self.radius ** 2 c = Circle(4) print(c.radius) print(c.area) print(c.area)#方法2def LazyProperty(func): attr_name = "_lazy_" + func.__name__ @property def wrap(self): if not hasattr(self, attr_name): setattr(self, attr_name, func(self)) return getattr(self, attr_name) return wrap class Circle(object): def __init__(self, radius): self.radius = radius @LazyProperty def area(self): print("come in") return 3.14 * self.radius ** 2 c = Circle(4) print(c.radius) print(c.area) print(c.area)View Codepython之懒惰属性(延迟初始化)
相关内容
- 解决python tkinter 与 sleep 延迟问题,,多线程(thread
- ArcGIS + Python 批量裁剪、添加X/Y坐标脚本,arcgispython,前
- python连接MySQL,, 再python3
- Python递归与迭代,Python递归,1、递归与迭代:递归
- Python中的函数与变量,,本节内容函数的定义方
- python 统计MySQL大于100万的表,pythonmysql,一、需求分析线
- Python数据类型-元组,python数据类型,元组的基本操作:获
- python学习随笔(三)_字符串,,字符串*** 是由一
- Python 异常处理,python异常处理,Python异常Py
- Python中模块(Module)和包(Package)的区别,,本文绝大部分
评论关闭