蚁群算法简介及应用,,蚂蚁几乎没有视力,但
蚁群算法简介及应用,,蚂蚁几乎没有视力,但
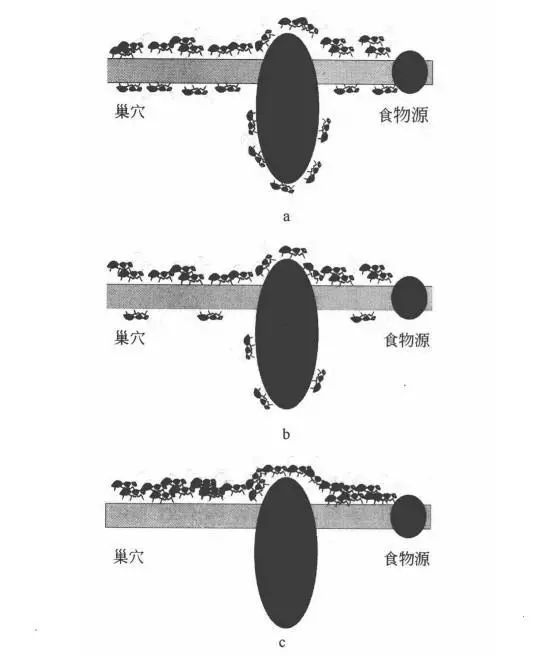
蚂蚁几乎没有视力,但他们却能够在黑暗的世界中找到食物,而且能够找到一条从洞穴到食物的最短路径。它们是如何做到的呢?
简介
由来
蚁群算法是一种用来寻找优化路径的概率型算法。它由Marco Dorigo于1992年在他的博士论文中提出,其灵感来源于蚂蚁在寻找食物过程中发现路径的行为。
这种算法具有分布计算、信息正反馈和启发式搜索的特征,本质上是进化算法中的一种启发式全局优化算法。
思想
将蚁群算法应用于解决优化问题的基本思路为:用蚂蚁的行走路径表示待优化问题的可行解,整个蚂蚁群体的所有路径构成待优化问题的解空间。路径较短的蚂蚁释放的信息素量较多,随着时间的推进,较短的路径上累积的信息素浓度逐渐增高,选择该路径的蚂蚁个数也愈来愈多。最终,整个蚂蚁会在正反馈的作用下集中到最佳的路径上,此时对应的便是待优化问题的最优解。
应用
蚁群算法应用广泛,如旅行商问题(traveling salesman problem,简称TSP)、指派问题、Job-shop调度问题、车辆路径问题(vehicle routing problem)、图着色问题(graph coloring problem)和网络路由问题(network routing problem)等等,下面以TSP的求解为例。
scikit-opt库实现
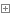
import numpy as npfrom scipy import spatialimport pandas as pdimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltnum_points = 25points_coordinate = np.random.rand(num_points, 2) # generate coordinate of pointsdistance_matrix = spatial.distance.cdist(points_coordinate, points_coordinate, metric=‘euclidean‘)def cal_total_distance(routine): num_points, = routine.shape return sum([distance_matrix[routine[i % num_points], routine[(i + 1) % num_points]] for i in range(num_points)])from sko.ACA import ACA_TSPaca = ACA_TSP(func=cal_total_distance, n_dim=num_points, size_pop=50, max_iter=200, distance_matrix=distance_matrix)best_x, best_y = aca.run()# %% Plotfig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2)best_points_ = np.concatenate([best_x, [best_x[0]]])best_points_coordinate = points_coordinate[best_points_, :]ax[0].plot(best_points_coordinate[:, 0], best_points_coordinate[:, 1], ‘o-r‘)pd.DataFrame(aca.y_best_history).cummin().plot(ax=ax[1])plt.show()View Code
Python实现

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-import randomimport copyimport timeimport sysimport mathimport tkinter #//GUI模块import threadingfrom functools import reduce # 参数‘‘‘ALPHA:信息启发因子,值越大,则蚂蚁选择之前走过的路径可能性就越大 ,值越小,则蚁群搜索范围就会减少,容易陷入局部最优BETA:Beta值越大,蚁群越就容易选择局部较短路径,这时算法收敛速度会 加快,但是随机性不高,容易得到局部的相对最优‘‘‘(ALPHA, BETA, RHO, Q) = (1.0,2.0,0.5,100.0)# 城市数,蚁群(city_num, ant_num) = (50,50)distance_x = [ 178,272,176,171,650,499,267,703,408,437,491,74,532, 416,626,42,271,359,163,508,229,576,147,560,35,714, 757,517,64,314,675,690,391,628,87,240,705,699,258, 428,614,36,360,482,666,597,209,201,492,294]distance_y = [ 170,395,198,151,242,556,57,401,305,421,267,105,525, 381,244,330,395,169,141,380,153,442,528,329,232,48, 498,265,343,120,165,50,433,63,491,275,348,222,288, 490,213,524,244,114,104,552,70,425,227,331]#城市距离和信息素distance_graph = [ [0.0 for col in range(city_num)] for raw in range(city_num)]pheromone_graph = [ [1.0 for col in range(city_num)] for raw in range(city_num)] #----------- 蚂蚁 -----------class Ant(object): # 初始化 def __init__(self,ID): self.ID = ID # ID self.__clean_data() # 随机初始化出生点 # 初始数据 def __clean_data(self): self.path = [] # 当前蚂蚁的路径 self.total_distance = 0.0 # 当前路径的总距离 self.move_count = 0 # 移动次数 self.current_city = -1 # 当前停留的城市 self.open_table_city = [True for i in range(city_num)] # 探索城市的状态 city_index = random.randint(0,city_num-1) # 随机初始出生点 self.current_city = city_index self.path.append(city_index) self.open_table_city[city_index] = False self.move_count = 1 # 选择下一个城市 def __choice_next_city(self): next_city = -1 select_citys_prob = [0.0 for i in range(city_num)] #存储去下个城市的概率 total_prob = 0.0 # 获取去下一个城市的概率 for i in range(city_num): if self.open_table_city[i]: try : # 计算概率:与信息素浓度成正比,与距离成反比 select_citys_prob[i] = pow(pheromone_graph[self.current_city][i], ALPHA) * pow((1.0/distance_graph[self.current_city][i]), BETA) total_prob += select_citys_prob[i] except ZeroDivisionError as e: print (‘Ant ID: {ID}, current city: {current}, target city: {target}‘.format(ID = self.ID, current = self.current_city, target = i)) sys.exit(1) # 轮盘选择城市 if total_prob > 0.0: # 产生一个随机概率,0.0-total_prob temp_prob = random.uniform(0.0, total_prob) for i in range(city_num): if self.open_table_city[i]: # 轮次相减 temp_prob -= select_citys_prob[i] if temp_prob < 0.0: next_city = i break # 未从概率产生,顺序选择一个未访问城市 # if next_city == -1: # for i in range(city_num): # if self.open_table_city[i]: # next_city = i # break if (next_city == -1): next_city = random.randint(0, city_num - 1) while ((self.open_table_city[next_city]) == False): # if==False,说明已经遍历过了 next_city = random.randint(0, city_num - 1) # 返回下一个城市序号 return next_city # 计算路径总距离 def __cal_total_distance(self): temp_distance = 0.0 for i in range(1, city_num): start, end = self.path[i], self.path[i-1] temp_distance += distance_graph[start][end] # 回路 end = self.path[0] temp_distance += distance_graph[start][end] self.total_distance = temp_distance # 移动操作 def __move(self, next_city): self.path.append(next_city) self.open_table_city[next_city] = False self.total_distance += distance_graph[self.current_city][next_city] self.current_city = next_city self.move_count += 1 # 搜索路径 def search_path(self): # 初始化数据 self.__clean_data() # 搜素路径,遍历完所有城市为止 while self.move_count < city_num: # 移动到下一个城市 next_city = self.__choice_next_city() self.__move(next_city) # 计算路径总长度 self.__cal_total_distance() #----------- TSP问题 ----------- class TSP(object): def __init__(self, root, width = 800, height = 600, n = city_num): # 创建画布 self.root = root self.width = width self.height = height # 城市数目初始化为city_num self.n = n # tkinter.Canvas self.canvas = tkinter.Canvas( root, width = self.width, height = self.height, bg = "#EBEBEB", # 背景白色 xscrollincrement = 1, yscrollincrement = 1 ) self.canvas.pack(expand = tkinter.YES, fill = tkinter.BOTH) self.title("TSP蚁群算法(n:初始化 e:开始搜索 s:停止搜索 q:退出程序)") self.__r = 5 self.__lock = threading.RLock() # 线程锁 self.__bindEvents() self.new() # 计算城市之间的距离 for i in range(city_num): for j in range(city_num): temp_distance = pow((distance_x[i] - distance_x[j]), 2) + pow((distance_y[i] - distance_y[j]), 2) temp_distance = pow(temp_distance, 0.5) distance_graph[i][j] =float(int(temp_distance + 0.5)) # 按键响应程序 def __bindEvents(self): self.root.bind("q", self.quite) # 退出程序 self.root.bind("n", self.new) # 初始化 self.root.bind("e", self.search_path) # 开始搜索 self.root.bind("s", self.stop) # 停止搜索 # 更改标题 def title(self, s): self.root.title(s) # 初始化 def new(self, evt = None): # 停止线程 self.__lock.acquire() self.__running = False self.__lock.release() self.clear() # 清除信息 self.nodes = [] # 节点坐标 self.nodes2 = [] # 节点对象 # 初始化城市节点 for i in range(len(distance_x)): # 在画布上随机初始坐标 x = distance_x[i] y = distance_y[i] self.nodes.append((x, y)) # 生成节点椭圆,半径为self.__r node = self.canvas.create_oval(x - self.__r, y - self.__r, x + self.__r, y + self.__r, fill = "#ff0000", # 填充红色 outline = "#000000", # 轮廓白色 tags = "node", ) self.nodes2.append(node) # 显示坐标 self.canvas.create_text(x,y-10, # 使用create_text方法在坐标(302,77)处绘制文字 text = ‘(‘+str(x)+‘,‘+str(y)+‘)‘, # 所绘制文字的内容 fill = ‘black‘ # 所绘制文字的颜色为灰色 ) # 顺序连接城市 #self.line(range(city_num)) # 初始城市之间的距离和信息素 for i in range(city_num): for j in range(city_num): pheromone_graph[i][j] = 1.0 self.ants = [Ant(ID) for ID in range(ant_num)] # 初始蚁群 self.best_ant = Ant(-1) # 初始最优解 self.best_ant.total_distance = 1 << 31 # 初始最大距离 self.iter = 1 # 初始化迭代次数 # 将节点按order顺序连线 def line(self, order): # 删除原线 self.canvas.delete("line") def line2(i1, i2): p1, p2 = self.nodes[i1], self.nodes[i2] self.canvas.create_line(p1, p2, fill = "#000000", tags = "line") return i2 # order[-1]为初始值 reduce(line2, order, order[-1]) # 清除画布 def clear(self): for item in self.canvas.find_all(): self.canvas.delete(item) # 退出程序 def quite(self, evt): self.__lock.acquire() self.__running = False self.__lock.release() self.root.destroy() print (u"\n程序已退出...") sys.exit() # 停止搜索 def stop(self, evt): self.__lock.acquire() self.__running = False self.__lock.release() # 开始搜索 def search_path(self, evt = None): # 开启线程 self.__lock.acquire() self.__running = True self.__lock.release() while self.__running: # 遍历每一只蚂蚁 for ant in self.ants: # 搜索一条路径 ant.search_path() # 与当前最优蚂蚁比较 if ant.total_distance < self.best_ant.total_distance: # 更新最优解 self.best_ant = copy.deepcopy(ant) # 更新信息素 self.__update_pheromone_gragh() print (u"迭代次数:",self.iter,u"最佳路径总距离:",int(self.best_ant.total_distance)) # 连线 self.line(self.best_ant.path) # 设置标题 self.title("TSP蚁群算法(n:随机初始 e:开始搜索 s:停止搜索 q:退出程序) 迭代次数: %d" % self.iter) # 更新画布 self.canvas.update() self.iter += 1 # 更新信息素 def __update_pheromone_gragh(self): # 获取每只蚂蚁在其路径上留下的信息素 temp_pheromone = [[0.0 for col in range(city_num)] for raw in range(city_num)] for ant in self.ants: for i in range(1,city_num): start, end = ant.path[i-1], ant.path[i] # 在路径上的每两个相邻城市间留下信息素,与路径总距离反比 temp_pheromone[start][end] += Q / ant.total_distance temp_pheromone[end][start] = temp_pheromone[start][end] # 更新所有城市之间的信息素,旧信息素衰减加上新迭代信息素 for i in range(city_num): for j in range(city_num): pheromone_graph[i][j] = pheromone_graph[i][j] * RHO + temp_pheromone[i][j] # 主循环 def mainloop(self): self.root.mainloop() #----------- 程序的入口处 ----------- if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: print (u""" -------------------------------------------------------- 程序:蚁群算法解决TPS问题程序 作者:许彬 日期:2015-12-10 语言:Python 2.7 -------------------------------------------------------- """) TSP(tkinter.Tk()).mainloop() View CodeC实现

#include<bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;#define sqr(x) ((x)*(x))#define eps 1e-8string file_name;int type;// type == 1 全矩阵, type == 2 二维欧拉距离int N;//城市数量double **dis;//城市间距离double **pheromone;//信息素double **herustic;//启发式值double **info;// info = pheromone ^ delta * herustic ^ betadouble pheromone_0;//pheromone初始值,这里是1 / (avg * N)其中avg为图网中所有边边权的平均数。int m;//种群数量int delta, beta;//参数double alpha;int *r1, *s, *r;//agent k的出发城市,下一个点,当前点。int MAX, iteration;//最大迭代次数,迭代计数变量set<int> empty, *J;struct vertex{ double x, y;// 城市坐标 int id;// 城市编号 int input(FILE *fp){ return fscanf(fp, "%d %lf %lf", &id, &x, &y);}}*node;typedef pair<int, int> pair_int;struct Tour{//路径 vector<pair_int> path;//path[i],存储一条边(r,s) double L; void clean(){ L = INF; path.clear(); path.shrink_to_fit(); }//清空 void calc(){ L = 0; int sz = path.size(); for (int i = 0; i < sz; i ++){ L += dis[path[i].first][path[i].second]; } }//计算长度 void push_back(int x, int y){ path.push_back(make_pair(x, y)); } int size(){ return (int)path.size(); } int r(int i){ return path[i].first; } int s(int i){ return path[i].second; } void print(FILE *fp){ int sz = path.size(); for (int i = 0; i < sz; i ++){ fprintf(fp, "%d->", path[i].first + 1); } fprintf(fp, "%d\n", path[sz - 1].second + 1); } bool operator <(const Tour &a)const{ return L < a.L; }//重载} *tour, best_so_far;double EUC_2D(const vertex &a, const vertex &b){ return sqrt(sqr(a.x - b.x) + sqr(a.y - b.y));}void io(){//输入 printf("input file_name and data type\n"); cin >> file_name >> type; FILE *fp = fopen(file_name.c_str(), "r"); fscanf(fp, "%d", &N); node = new vertex[N + 5]; dis = new double*[N + 5]; double tmp = 0; int cnt = 0; if (type == 1){ for (int i = 0; i < N; i ++){ dis[i] = new double[N]; for (int j = 0; j < N; j ++){ fscanf(fp, "%lf", &dis[i][j]); tmp += i != j ? dis[i][j] : 0;// i == j的时候dis不存在,所以不考虑。 cnt += i != j ? 1 : 0;// i == j的时候dis不存在,所以不考虑。 } } }else{ for (int i = 0; i < N; i ++) node[i].input(fp); for (int i = 0; i < N; i ++){ dis[i] = new double[N]; for (int j = 0; j < N; j ++){ dis[i][j] = EUC_2D(node[i], node[j]);// 计算距离 tmp += i != j ? dis[i][j] : 0;// i == j的时候 dis不存在,所以不考虑。 cnt += i != j ? 1 : 0;// i == j的时候dis不存在,所以不考虑。 } } } pheromone_0 = (double)cnt / (tmp * N);//pheromone初始值,这里是1 / (avg * N)其中avg为图网中所有边边权的平均数。 fclose(fp); return;}void init(){//初始化 alpha = 0.1;//evaporation parameter,挥发参数,每次信息素要挥发的量 delta = 1; beta = 6;// delta 和 beta分别表示pheromones和herustic的比重 m = N; pheromone = new double*[N + 5]; herustic = new double*[N + 5]; info = new double*[N + 5]; r1 = new int[N + 5]; r = new int[N + 5]; s = new int[N + 5]; J = new set<int>[N + 5]; empty.clear(); for (int i = 0; i < N; i ++){ pheromone[i] = new double[N + 5]; herustic[i] = new double[N + 5]; info[i] = new double[N + 5]; empty.insert(i); for (int j = 0; j < N; j ++){ pheromone[i][j] = pheromone_0; herustic[i][j] = 1 / (dis[i][j] + eps);//加一个小数eps,防止被零除 } } best_so_far.clean(); iteration = 0; MAX = N * N;}double power(double x, int y){//快速幂,计算x ^ y,时间复杂度O(logn),感兴趣可以百度 double ans = 1; while (y){ if (y & 1) ans *= x; x *= x; y >>= 1; } return ans;}void reset(){ tour = new Tour[m + 5]; for (int i = 0; i < N; i ++){ tour[i].clean(); r1[i] = i;//初始化出发城市, J[i] = empty; J[i].erase(r1[i]);//初始化agent i需要访问的城 市 r[i] = r1[i];//当前在出发点 } for (int i = 0; i < N; i ++) for (int j = 0; j < N; j ++){ info[i][j] = power(pheromone[i][j], delta) * power(herustic[i][j], beta); }//选择公式}int select_next(int k){ if (J[k].empty()) return r1[k]; //如果J是空的,那么返回出发点城市 double rnd = (double)(rand()) / (double)RAND_MAX;//产生0..1的随机数 set<int>::iterator it = J[k].begin(); double sum_prob = 0, sum = 0; for (; it != J[k].end(); it ++){ sum += info[r[k]][*it]; }//计算概率分布 rnd *= sum; it = J[k].begin(); for (; it != J[k].end(); it ++){ sum_prob += info[r[k]][*it]; if (sum_prob >= rnd){ return *it; } }//依照概率选取下一步城市}void construct_solution(){ for (int i = 0; i < N; i ++){ for (int k = 0; k < m; k ++){ int next = select_next(k);//选择下一步的最优决策 J[k].erase(next); s[k] = next; tour[k].push_back(r[k], s[k]); r[k] = s[k]; } }}void update_pheromone(){ Tour now_best; now_best.clean();//初始化 for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++){ tour[i].calc(); if (tour[i] < now_best) now_best = tour[i];//寻找当前迭代最优解 } if (now_best < best_so_far){ best_so_far = now_best;//更新最优解 } for (int i = 0; i < N; i ++) for (int j = 0; j < N; j ++) pheromone[i][j] *= (1 - alpha);//信息素挥发 int sz = now_best.size(); for (int i = 0; i < sz; i ++){ pheromone[now_best.r(i)][now_best.s(i)] += 1. / (double)now_best.L; pheromone[now_best.s(i)][now_best.r(i)] = pheromone[now_best.r(i)][now_best.s(i)];// 对称 }//更新信息素含量}int main(){ srand((unsigned) time(0));//初始化随机种子 io(); init(); double last = INF; int bad_times = 0; for (; iteration < MAX; iteration ++){ if (bad_times > N) break;//进入局部最优 reset();//初始化agent信息 construct_solution();//对于所有的agent构造一个完整的tour update_pheromone();//更新信息素 printf("iteration %d:best_so_far = %.2f\n", iteration, best_so_far.L); if (last > best_so_far.L) last = best_so_far.L, bad_times = 0; else bad_times ++;//记录当前未更新代数,若迭代多次未更新,认为进入局部最优 } printf("best_so_far = %.2f\n", best_so_far.L);// 输出目标值 best_so_far.print(stdout);//输出路径}算例演示例一 满秩矩阵式(type = 1)输入文件格式为:File_name File_typesalesman.in 150 1 2 2 32 0 3 4 23 2 0 4 13 4 5 0 52 4 1 4 0输出结果为:opt_solution:11例二 二维坐标式(type = 2)输入文件格式为:File_name File_typeKroA100.tsp 21001 1380 9392 2848 963 3510 16714 457 3345 3888 6666 984 9657 2721 14828 1286 5259 2716 143210 738 132511 1251 183212 2728 169813 3815 16914 3683 153315 1247 194516 123 86217 1234 194618 252 124019 611 67320 2576 167621 928 170022 53 85723 1807 171124 274 142025 2574 94626 178 2427 2678 182528 1795 96229 3384 149830 3520 107931 1256 6132 1424 172833 3913 19234 3085 152835 2573 196936 463 167037 3875 59838 298 151339 3479 82140 2542 23641 3955 174342 1323 28043 3447 183044 2936 33745 1621 183046 3373 164647 1393 136848 3874 131849 938 95550 3022 47451 2482 118352 3854 92353 376 82554 2519 13555 2945 162256 953 26857 2628 147958 2097 98159 890 184660 2139 180661 2421 100762 2290 181063 1115 105264 2588 30265 327 26566 241 34167 1917 68768 2991 79269 2573 59970 19 67471 3911 167372 872 155973 2863 55874 929 176675 839 62076 3893 10277 2178 161978 3822 89979 378 104880 1178 10081 2599 90182 3416 14383 2961 160584 611 138485 3113 88586 2597 183087 2586 128688 161 90689 1429 13490 742 102591 1625 165192 1187 70693 1787 100994 22 98795 3640 4396 3756 88297 776 39298 1724 164299 198 1810100 3950 1558输出结果为:best_known_solution: 21282View Code参考链接:
1. 百度百科-蚁群算法
2. 掘金-10分钟搞懂蚁群算法
3. scikit-opt官方文档-ACA部分
4. CSDN-fanxin_i-蚁群算法原理及实现(Python)
5. 知乎-数据魔法师-十分钟快速get蚁群算法(附C代码)
蚁群算法简介及应用
相关内容
- Python入门《父与子的编程之旅第2版》+《教孩子学编程
- python求道03日,,1.关于int的使用
- Momentum(动量)方法的python实现,,Momentum方法
- python_面向对象编程,,初始面向对象一、类的
- Python--基础总结(二),,模块操作什么是模块?
- 不同 Python 数据类型的搜寻,,不同 Python
- 使用Python读写Kafka,,本篇会给出如何使用p
- ubuntu14.04上安装python的numpy、scipy、matplotlib、pandas库,
- 2020年一线大厂月薪35K的Python开发要求,,为什么程序员
- python3之字符串常用操作练习补充二,,字符串常用操作
评论关闭